Family Overview
Our diamond-based cutting tools are designed for high productivity and extended tool life. Usually, they are able to outperform ceramics-based solutions, thereby reducing production costs. Since diamond is the hardest material available, you should consider these inserts whenever exceptional abrasion resistance is required. They are compatible with standard tool holders by other, leading manufacturers.
The inserts are available in two cutting materials: Polycrystalline diamonds (PCD) which are made of diamond particles sintered together with the help of a metallic binder, and CVD thick-film diamonds which are manufactured through the use of laser equipment.
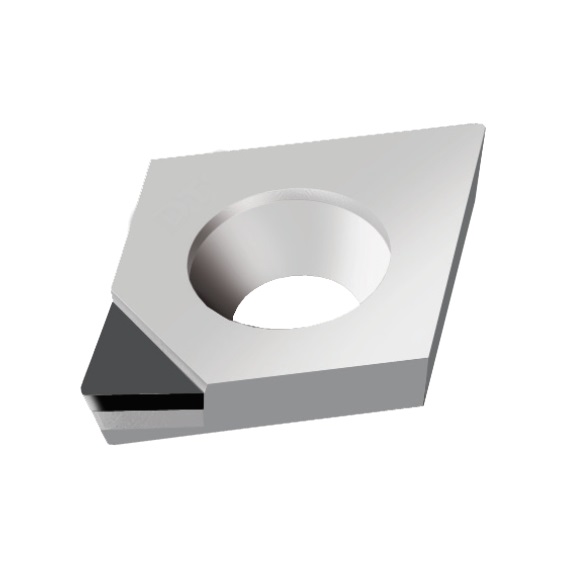
CCGT INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 80° cutting corner angle, and a single cutting tip. These inserts have a positive rake angle, and a relief angle of 7°.
Cutting Material(s):
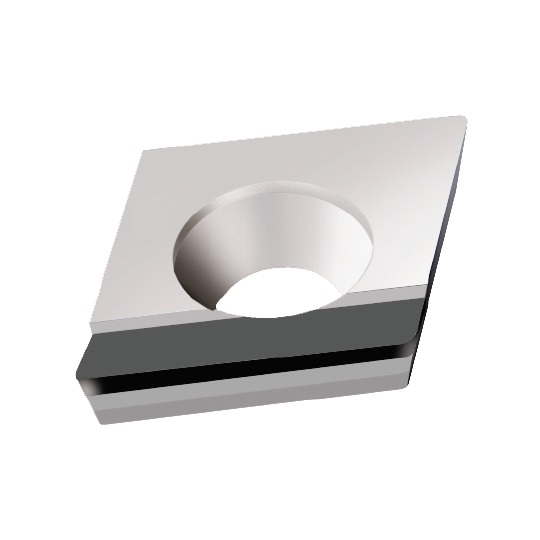

CCGT-GS INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 80° cutting corner angle, and a single cutting edge. These inserts have a positive rake angle, and a relief angle of 7°.
Cutting Material(s):
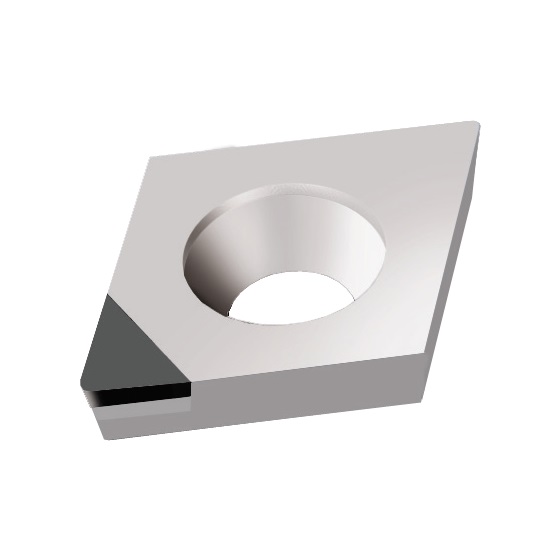
CCGW INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 80° cutting corner angle, and a single cutting tip. These inserts have a neutral rake angle, and a relief angle of 7°.
Features:
- Two chip breaker styles available: Type F for finishing applications, and type R for roughing applications
- Wiper geometry versions available; wiper inserts can be used for both right-hand and left-hand jobs
Note:
- The CCGW 060201 insert is only available without chip breakers, and with a CVD cutting tip
Cutting Material(s):
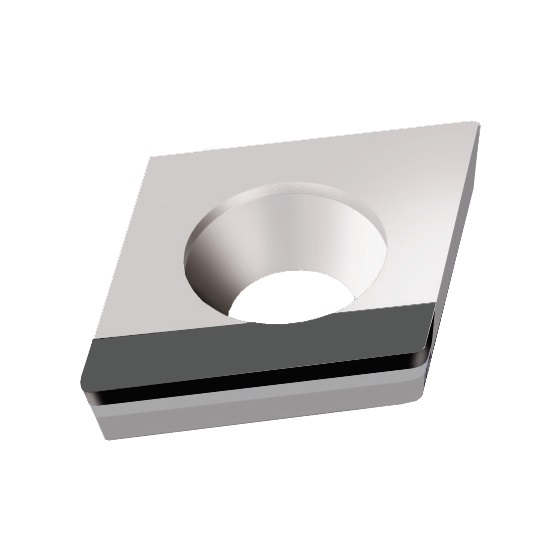

CCGW-GS INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 80° cutting corner angle, and a single cutting edge. These inserts have a neutral rake angle, and a relief angle of 7°.
Features:
- Two chip breaker styles available: Type F for finishing applications, and type R for roughing applications
- Variants for both right-hand and left-hand jobs are available
Cutting Material(s):
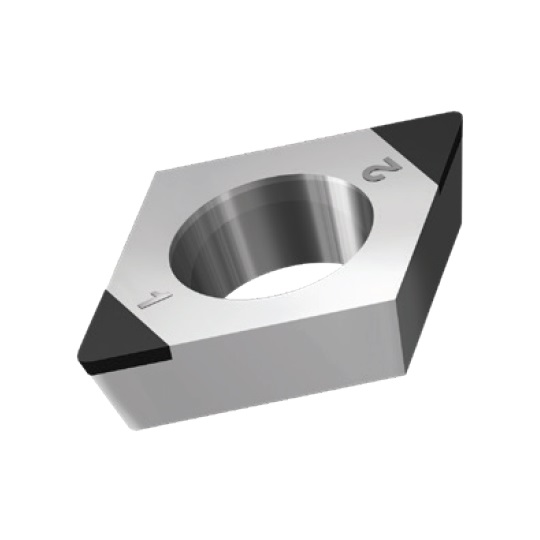

CDGW INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 80° cutting corner angle, and two cutting tips. These inserts have a neutral rake angle, and a relief angle of 15°.
Cutting Material(s):
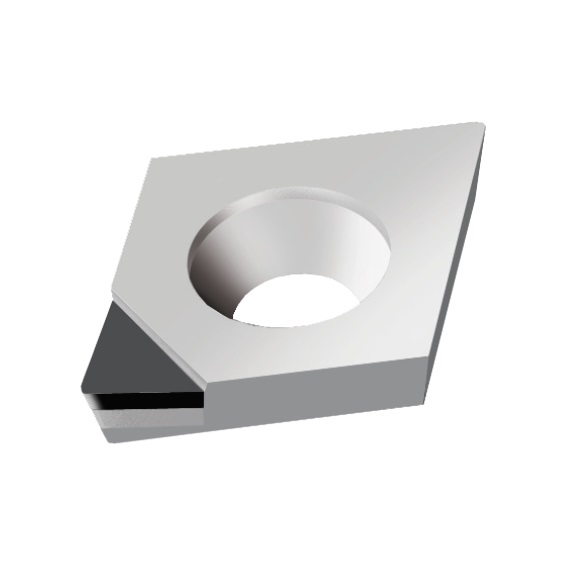
CPGT INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 80° cutting corner angle, and a single cutting tip. These inserts have a positive rake angle, and a relief angle of 11°.
Cutting Material(s):
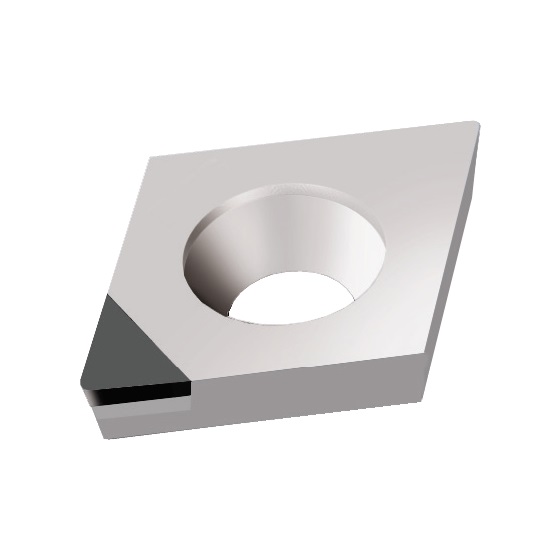
CPGW INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 80° cutting corner angle, and a single cutting tip. These inserts have a neutral rake angle, and a relief angle of 11°.
Features:
- Two chip breaker styles available: Type F for finishing applications, and type R for roughing applications
Note:
- The CPGW 060201 and CPGW 09T301 inserts are only available without chip breakers, and with a CVD cutting tip
Cutting Material(s):
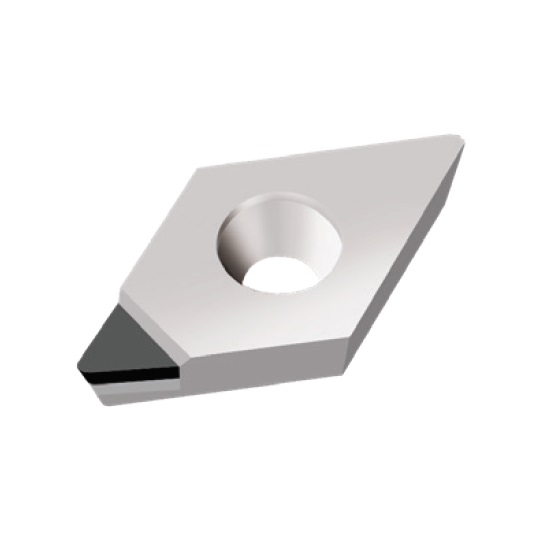
DCGT INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 55° cutting corner angle, and a single cutting tip. These inserts have a positive rake angle, and a relief angle of 7°.
Features:
- Wiper geometry versions available; wiper inserts can be used for both right-hand and left-hand jobs
Cutting Material(s):
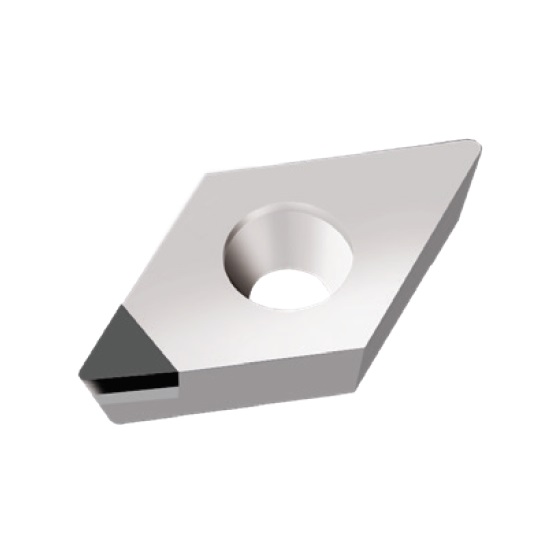
DCGW INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 55° cutting corner angle, and a single cutting tip. These inserts have a neutral rake angle, and a relief angle of 7°.
Features:
- Two chip breaker styles available: Type F for finishing applications, and type R for roughing applications
- Wiper geometry versions available; wiper inserts can be used for both right-hand and left-hand jobs
Note:
- The DCGW 070201 and DCGW 11T301 inserts are not available with chip breakers
Cutting Material(s):
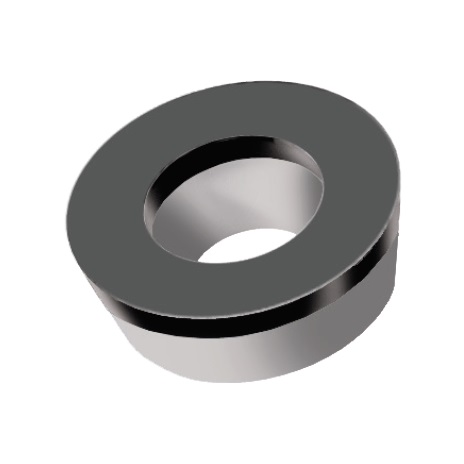

RCGW INSERTS
A line of round, full-face inserts with a relief angle of 7°.
Features:
- Two chip breaker styles available: Type F for finishing applications, and type R for roughing applications
Cutting Material(s):
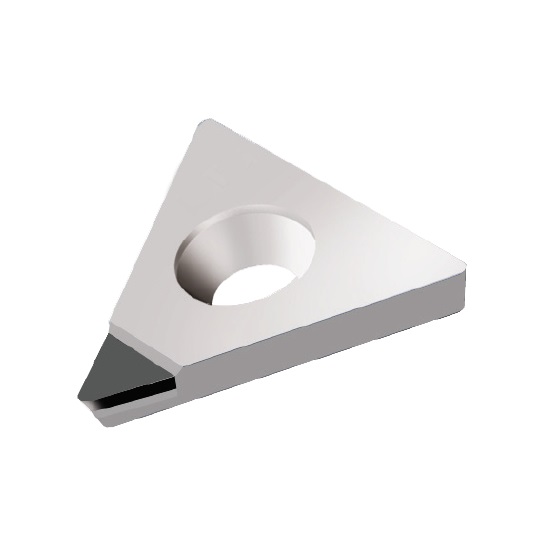

TCGT INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 60° cutting corner angle, and a single cutting tip. These inserts have a positive rake angle, and a relief angle of 7°.
Cutting Material(s):
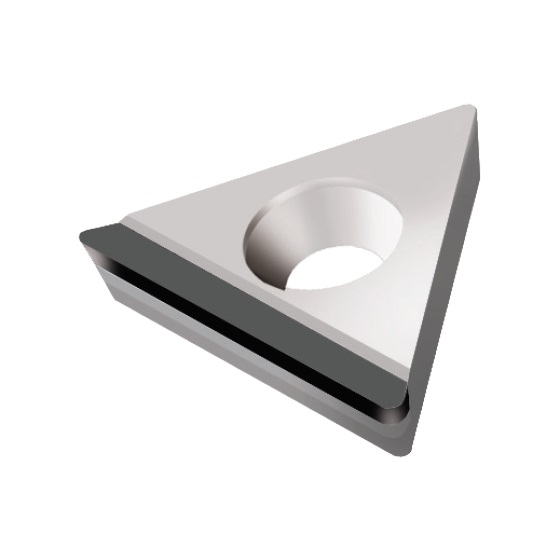

TCGT-GS INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 60° cutting corner angle, and a single cutting edge. These inserts have a positive rake angle, and a relief angle of 7°.
Cutting Material(s):
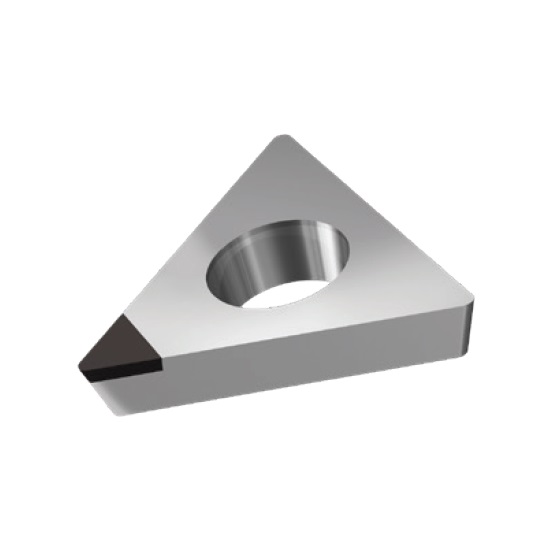

TCGW INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 60° cutting corner angle, and a single cutting tip. These inserts have a neutral rake angle, and a relief angle of 7°.
Features:
- Two chip breaker styles available: Type F for finishing applications, and type R for roughing applications
Note:
- The TCGW 090201 and TCGW 110201 inserts are not available with chip breakers
Cutting Material(s):
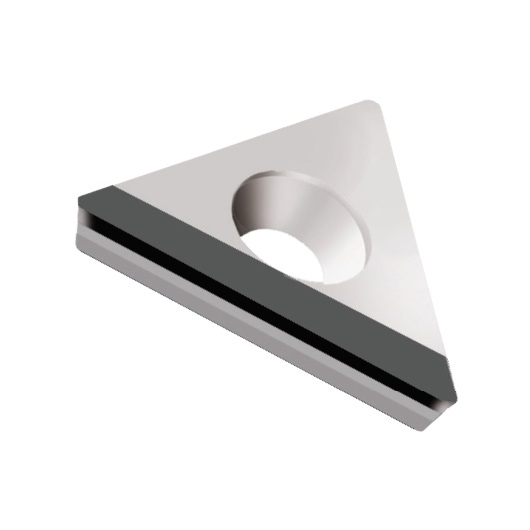

TCGW-GS INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 60° cutting corner angle, and a single cutting edge. These inserts have a neutral rake angle, and a relief angle of 7°.
Features:
- Two chip breaker styles available: Type F for finishing applications, and type R for roughing applications
Cutting Material(s):
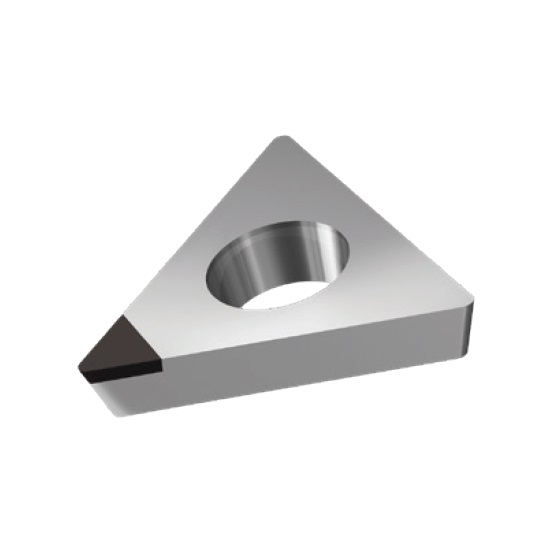

TPGW INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 60° cutting corner angle, and a single cutting tip. These inserts have a neutral rake angle, and a relief angle of 11°.
Features:
- Two chip breaker styles available: Type F for finishing applications, and type R for roughing applications
Note:
- The TPGW 06T101 insert is not available with chip breakers
Cutting Material(s):
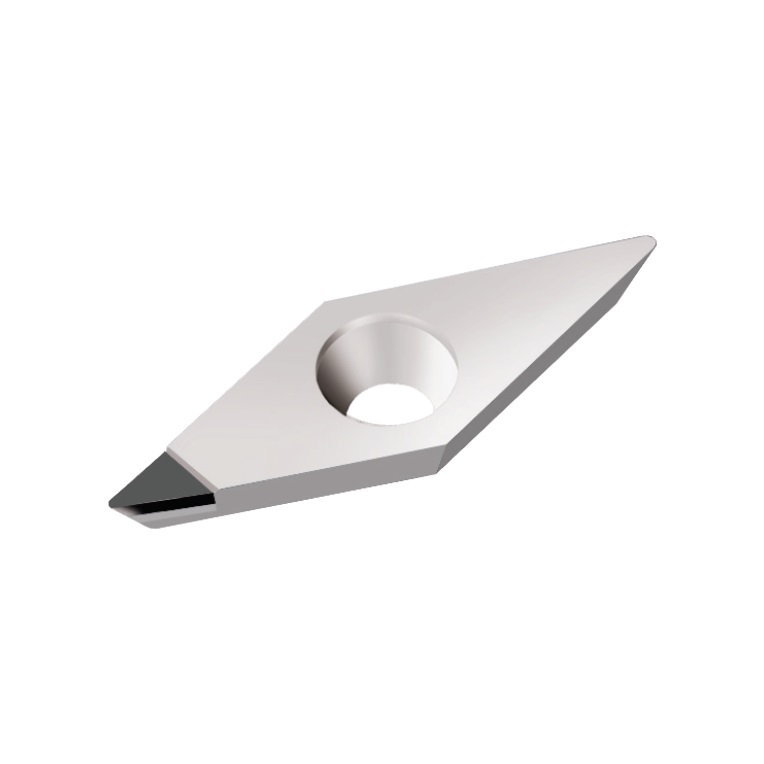

VCGT INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 35° cutting corner angle, and a single cutting tip. These inserts have a positive rake angle, and a relief angle of 7°.
Cutting Material(s):
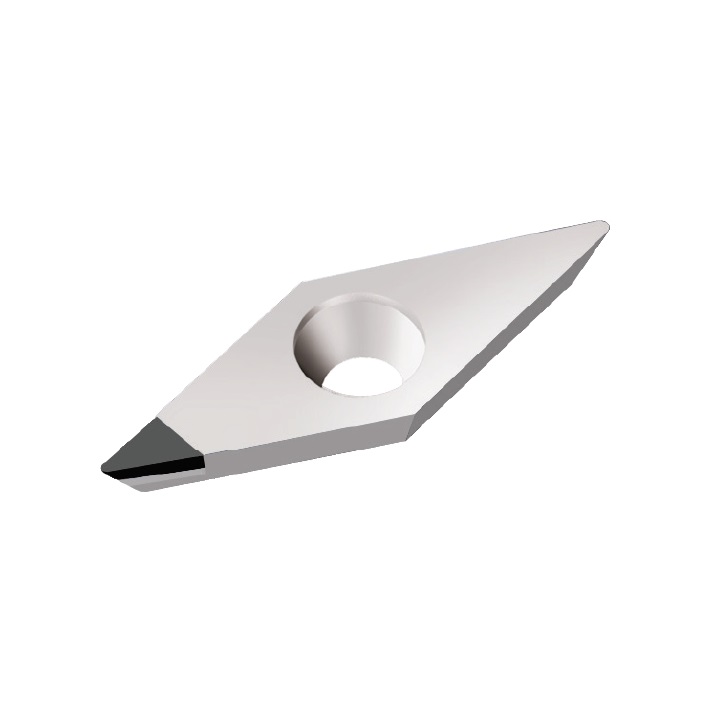

VCGW INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 35° cutting corner angle, and a single cutting tip. These inserts have a neutral rake angle, and a relief angle of 7°.
Features:
- Two chip breaker styles available: Type F for finishing applications, and type R for roughing applications
Note:
- The VCGW 070201, VCGW 110301, and VCGW 160401 inserts are not available with chip breakers
Cutting Material(s):
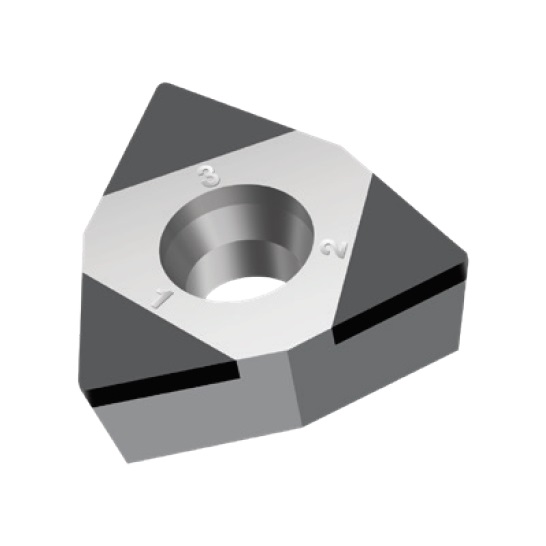
WCGW INSERTS
A line of inserts with a 80° cutting corner angle, and three cutting tips. These inserts have a neutral rake angle, and a relief angle of 7°.
Cutting Material(s):

